

Increasing the Prefix is also the way by which Subnetting occurs, a vital part of networking through which a larger network is divided into smaller networks.
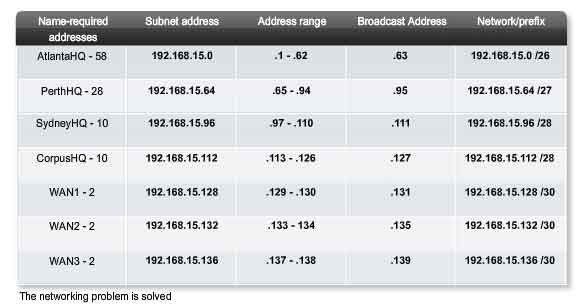
In this way, the Prefix is abbreviated as a slash & the total number of 1 bits. Also known as the Prefix, the Network Mask appears similar to a host IPv4 address, but contains a specific number of 1 bits from left to right. Network Ranges are commonly defined by the Network ID and Network Mask. While neither should ever be used for Host addresses, they are referenced by Hosts for both local & internetwork communication, as well as admins, when creating networks. The first address in every network is called the Network ID, while the last address in every network is called the Broadcast ID.
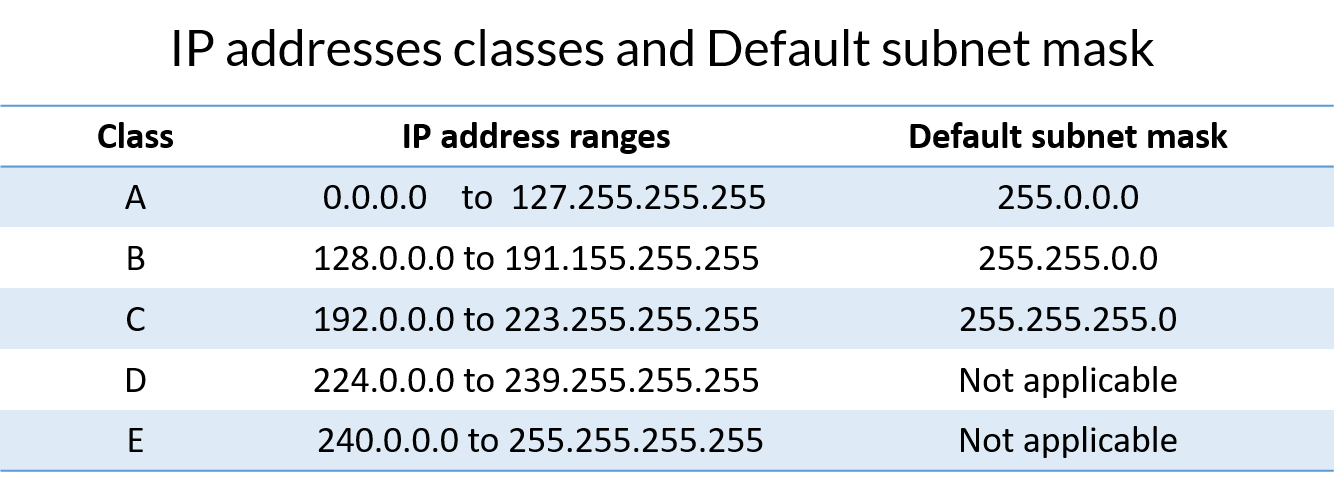
Compared to private IP addresses, which are re-used on all LANs, public IPv4 addresses are generally assigned to unique, WAN-facing interfaces. IP addresses falling outside these ranges are considered either "reserved", or public addresses to be used on the public Internet. Private IPv4 addresses consist of three n etwork IP ranges, listed from largest to smallest below: Private addresses (commonly called RFC 1918 addresses) are assigned to IPv4 Hosts on every Local Area Network. IPv4 Addresses specify four octets of summed bit values, where each bit value represents 2-to-the-power-of-its position in the octet. From left-to-right within the octet, bits carry a value, 2-to-the-power-of-8, all the way to 2-to-the-power-of-0. For example, the address 0.0.0.0 would contain all 8 zero bits across each octet, while the address 255.255.255.255 would contain 8 one bits across each octet.Ĭhart showing the IPv4 Address 10.5.37.156 (decimal notation) expressed in binary notation.īroadly speaking, there are two types of IPv4 addresses. IPv4 specifies the system of addressing for Hosts to identify themselves on the Network. Table of ContentsĪ Node wishing to communicate on the Network receives a unique Network Address, and is formally called a Host. Find a complete introductory guide on Routing and Switching in our Ubiquiti Broadband Routing & Switching Specialist (UBRSS) guide, downloadable in our Training section.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
